Meta tags can be a valuable tool in your SEO arsenal.
They are easy to use and can help you increase search engine rankings.
Do you want to learn how they work?
This post will discuss everything you need to know about them.
Contents:
What Are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are HTML elements that provide information about a page. Search engines use them to index and rank websites.
They may include the title, description, and other information about your content.

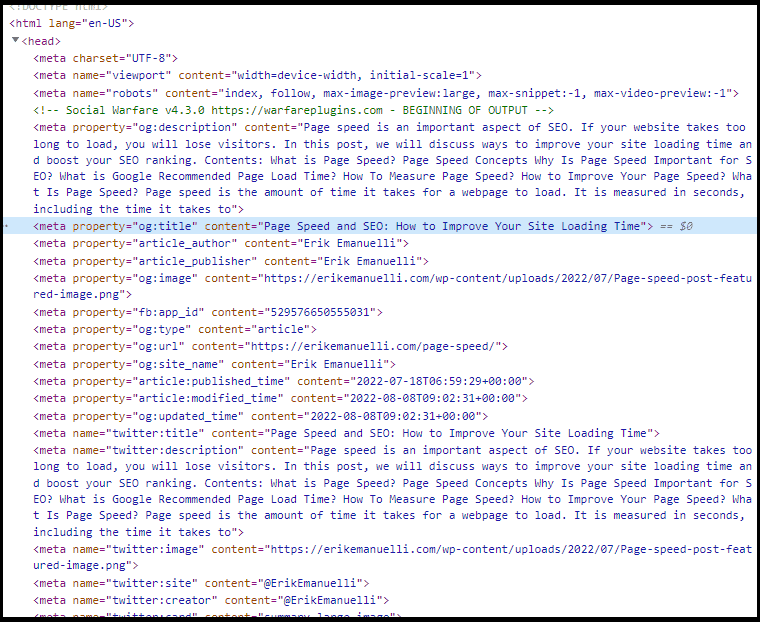
The most popular meta tags are:
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Robot meta tags
- Viewport meta tags
Are you curious to know more?
Then, keep reading.
Why Are Meta Tags Important for SEO?
Meta tags are essential for SEO because they help search engines understand your website.
They may also help you rank better on search engine results pages.
Let me show you how.
Title tags and meta descriptions are two of the most important meta tags for SEO.
The first ones tell search engines what your website is about. While the second ones give a summary of what is included in your web page.

So, if they are well-optimized, you will have more chances to increase your organic CTR and rank higher in SERPs.
As if that’s not enough, meta tags communicate with search engine bots.
Want to know a secret?
You should pay attention to your robot meta tags. If you badly set them up, either by mistake or lack of information, you can destroy the entire visibility of your website.
How?
For example, by giving the “content=”noindex” command:

This will tell search engine robots not to index your web page. As a result, your web page will likely not appear in SERPs.
Title Tags
They are HTML elements that specify the title of a web page (which are then displayed in SERPs).
They are also used by social media platforms to show information about your page when it is shared.
Now, pay attention to this.
Your title tag should be:
- Unique: this means that it should not be the same as the title tag of another web page
- Accurate: it should accurately describe your content
- Relevant: it should include the keywords you are targeting
- Descriptive: the description of your page should be brief but accurate

So, how can you achieve that?

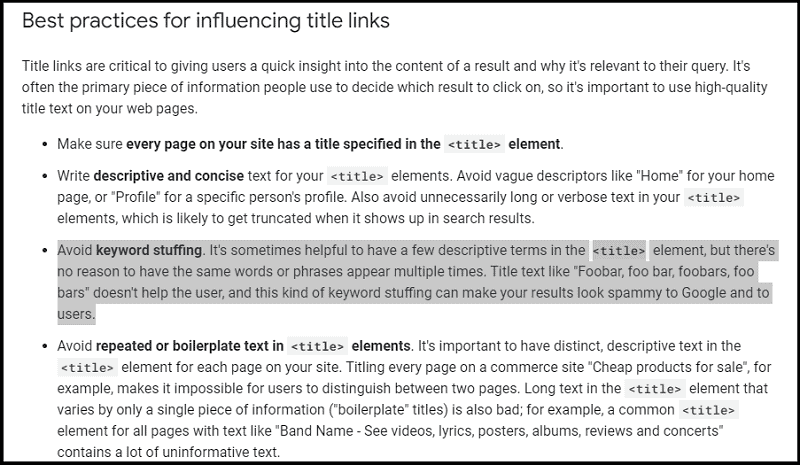
- Keep your title tag under 60 characters
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Use title case
- Focus on search intent
- Avoid clickbait titles
- Write something catchy
- Experiment with brackets
Meta Description Tags
A meta description is an HTML element that specifies a summary of a web page (and it’s what you want to be seen by people in the SERPs).
Now, do you want to know a secret?
It “can be used” by Google.
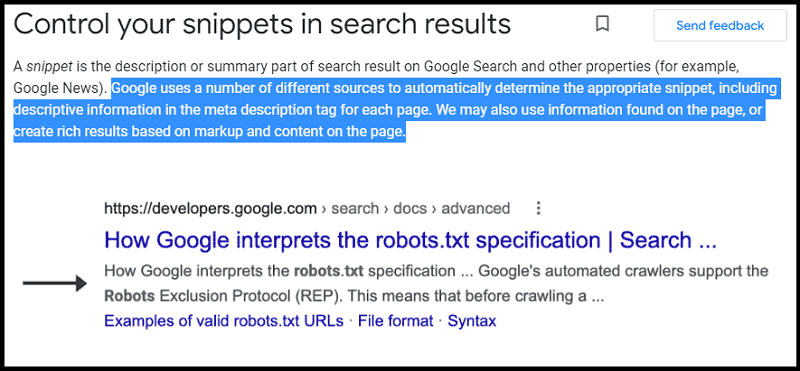
What does it mean?

And it turns out Google rewrites meta descriptions more than 62% of the time.
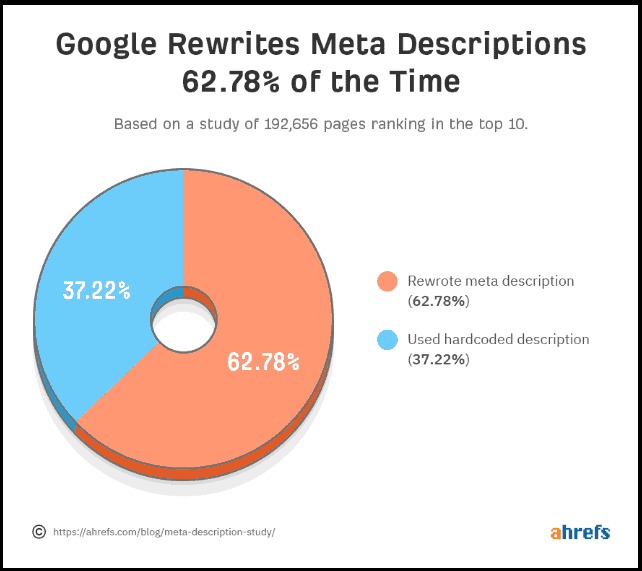
This SEO statistic comes from Ahrefs research and shows that Google produces descriptions automatically from the content of the page if it feels that those generated by webmasters are of poor quality or unrelated to the user’s query.
So, remember these best practices when creating meta descriptions for your content:
- Keep them under 155 characters
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Use bucket brigade words
- Make them interesting and informative
- Write sentence case
- Focus on search intent
- Create unique descriptions
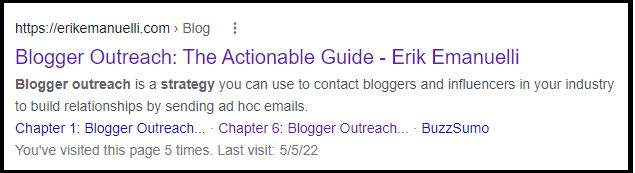
And in case you are wondering about my experience, here’s what my off-page SEO post looks like on Google:

Robot Meta Tags
A robot meta tag is an HTML element that specifies whether search engine robots should index a web page and follow its links.
OK, I know what you’re thinking:
all the pages and links you create are followed by default by search bots and crawlers.

- Index: this tells search engines to index a web page
- Follow: this allows web crawlers to follow the links on a web page
- Noarchive: this gives the command to search engine bots not to save a cached copy of your web page
- Noindex: this informs search bots not to index a web page
- Nofollow: this instructs search engines not to follow the links on a web page
For example, a command to tell web crawlers not to index a web page could look like this:

So, what does this mean for you?
It means that you should pay attention to the instructions you give to search engines.
In fact, robot meta tags instruct how Google crawls pages on your website.
For instance, you may want to use them to avoid duplicate content issues.
Some other times when you need to use robot meta tags include:
- When you are developing a website and don’t want search engines to index it until it’s ready
- If you have pages with sensitive information that you don’t want to be indexed
- When you have pages that are not valuable for SEO purposes and thus there is no need to index them
Robot Meta Tags VS Robots.txt
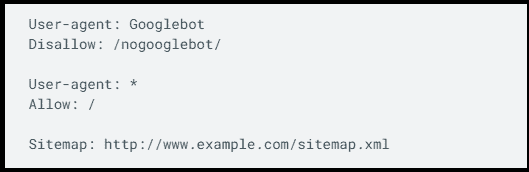
The robots.txt is a text file that you can create to instruct search engine bots which pages on your website should be indexed and which ones should not.
Do you want to learn more about it?
Here is an example:
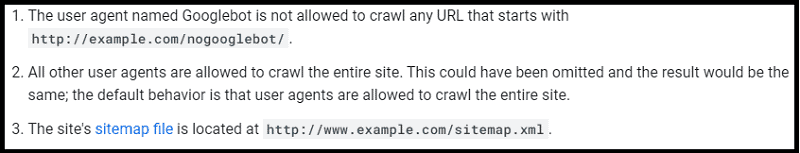
And here you can find its meaning (as officially explained by Google):

Viewport Meta Tag
The viewport meta tag is an HTML element that specifies the width and initial scale of a web page.
It is used to control how your web page is displayed on mobile devices.
If you don’t specify a viewport, mobile devices will assume that your web page is designed for desktop computers and will not display it correctly.
Here is an example:

As you can see, the viewport meta tag has two attributes: width and initial-scale.
The width attribute specifies the width of the viewport in pixels. The initial-scale specifies the initial zoom level of the page.
You can also use other values such as minimum-scale, maximum-scale, and user-scalable.

If you want to learn more about the viewport meta tag, I recommend reading the W3Schools guide.
How to Write Meta Tags
Do you know that 25.02% of the top-ranking pages do not have a meta description?
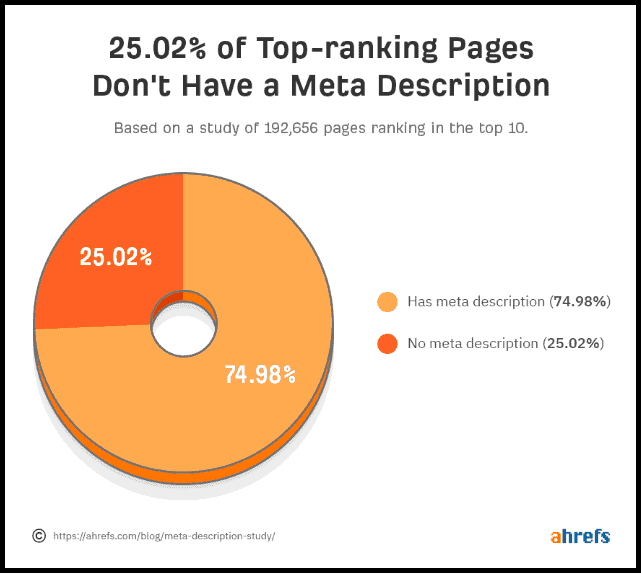
This Ahrefs study shows that it’s essential to learn how to write useful meta tags.
Now, if you want to manually add the HTML code of SEO meta tags, you should place it in the “head” section of your website:
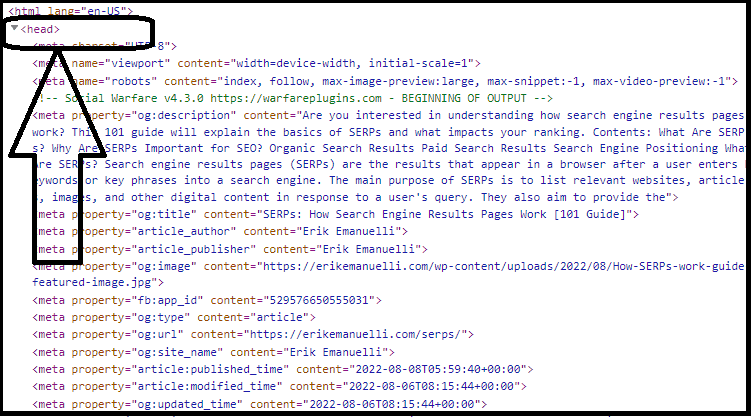

Once you install and activate the plugin, it will add an SEO section below each post, where you can add information about your content.
Here’s how it’s easy to set it up, based on my experience.
For example, to add the title tag, you need to scroll down to the SEO section and click on the “SEO title” field:
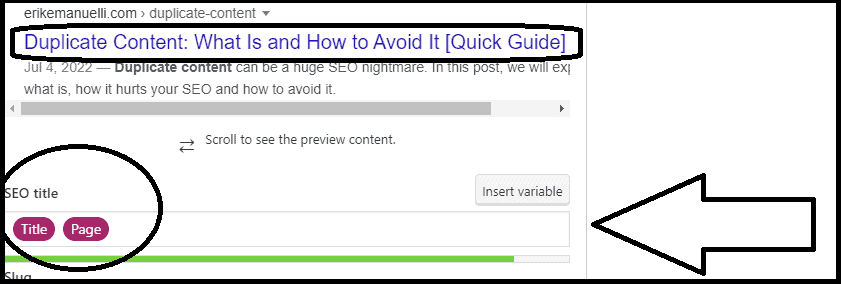
If you don’t, the plugin will automatically use the title of your blog post.
To add the meta description, you need to scroll down to the SEO section and add the information in the proper field:
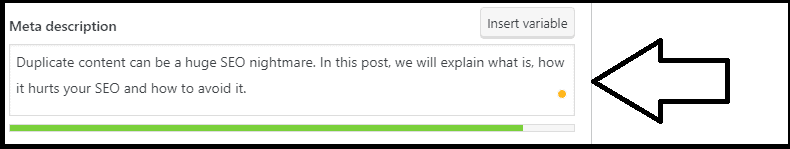
Finally, if you look into the “Advanced” section, you can edit robot meta tags:

Regarding the viewport meta tag, if you don’t want to mess up your site code, you just need to install a responsive theme, as I did for my site (I use the Genesis framework).
Tip: if you need help checking meta tags, I recommend Chrome extensions.
Full List of Meta Tags
Including a meta tag on your website is not a guarantee that Google will index or rank your pages.
However, it is still a good idea to include all the information that is relevant to your website.

- Title tag: to name a web page for search engines
- Meta description: to describe your content for search engines
- Robot meta tags: to index or not your website
- Viewport meta tag: to instruct how to render a page on mobile
- Nofollow, sponsored, and user-generated content meta tags: to control links
- Twitter cards meta tags and Open Graph meta tags: to share your content on social media
- Language meta-tags: to indicate the content language of the page
- Notranslate meta tag: to order Google to not automatically generate a translation
- Nositelinkssearchbox meta-tag: to not display the sitelinks search box
- Meta charset tag: to tell the character encoding of a website
- Meta refresh tag: to transfer the user to a new URL after a certain time, usually from a redirection (you should use a 301 redirect, instead)
Other meta tags, not essential to your SEO strategy:
- Meta keywords: used to tell search engines what your content was about (in 2009, Google declared to no longer use them)
- Author meta tag: to inform about the author of a page
- Copyright meta tag: to instruct about the owner of the rights of a page
- Meta name rating tag: to specify adult content
- Date meta tags: to tell the date of the content
SEO Meta Tags FAQs
Q: Does Google ignore meta tags?
A: No, Google does not ignore meta tags. While some of them are no longer seen as useful by search engines, many other ones can be very helpful when it comes to SEO. Most importantly these include the title tag and the meta description.
Q: Should I use a plugin for my SEO Meta Tags?
A: Yes, using a plugin is the easiest way to manage your meta tags. It also allows you to make changes whenever needed. If you are using WordPress, Yoast SEO is one of the best choices.
Q: Do I need to put meta tags on every page?
A: Yes, you should add meta tags to each page of your website. And it should be unique. This will help search engines understand what the content is about and rank your pages accordingly.
Q: How can I check my meta tags?
A: You can use a variety of tools to check your meta tags. Google Search Console offers great features for checking them. Additionally, you can also use Chrome extensions such as SEO META in 1 CLICK.
Before You Go
As you have seen, meta tags are something that you need to care about, if you are running a website.
But wait!
There’s much more than that to improve your listings on search engines!
Be sure to read these guides to learn how:
Now, it’s over to you.
Which techniques can you share to improve your SEO?
Let me know in the comments below.

Hello Erik,
Meta Tag plays a great role in increasing CTR. Its very important to write a good meta description for your blog posts that increases the Search Clicks. You have shared very helpful guide here
Regards,
Vishwajeet Kumar
Hi Vishwajeet,
based on your blogging experience,
what was the most performing strategy you adopted to increase organic CTR by optimizing meta tags?